Ten years ago I used to hear consultants advise against the implementation of electronic Kanban and encourage the use of physical cards and boards, as in the early days of the creation of this system. They avoided using technology so as not to bring unnecessary complexity to the factory floor and continued to focus on Lean, whether developing people, training them in identifying and solving problems or continuously improving processes. Here we notice an interesting mental model: the view that technology introduces complexity, while Lean is related to simplifying processes.
However, what if technology helped simplify, eliminate waste and add value to customer processes? Would this clash have a truce and would Lean and Technology be allies? It is this cooperation that we will explore in this article! We will show how technological advances have simplified digital transformation in Lean management and share examples that can increase your gains.
Before the jump, the first step…
Remembering the purpose of Lean and applying it is the first step to making this alliance viable. As you know, the basic principle of Lean starts with adding value to the customer, that is, everything that does not add value is seen as waste as it generates costs, consumes time and resources. Not applying Lean is a serious risk of investing in technologies automating waste.
An additional benefit of Lean is the reduction in the leadtime of implementing new technologies as its tools, such as standards and quality systems at the source, speed up the process of identifying and automating routines that will be translated into the digital environment. In other words, Lean ends up being a prerequisite for the company’s digital transformation, making it more efficient.
The leap of Lean through Digital Transformation
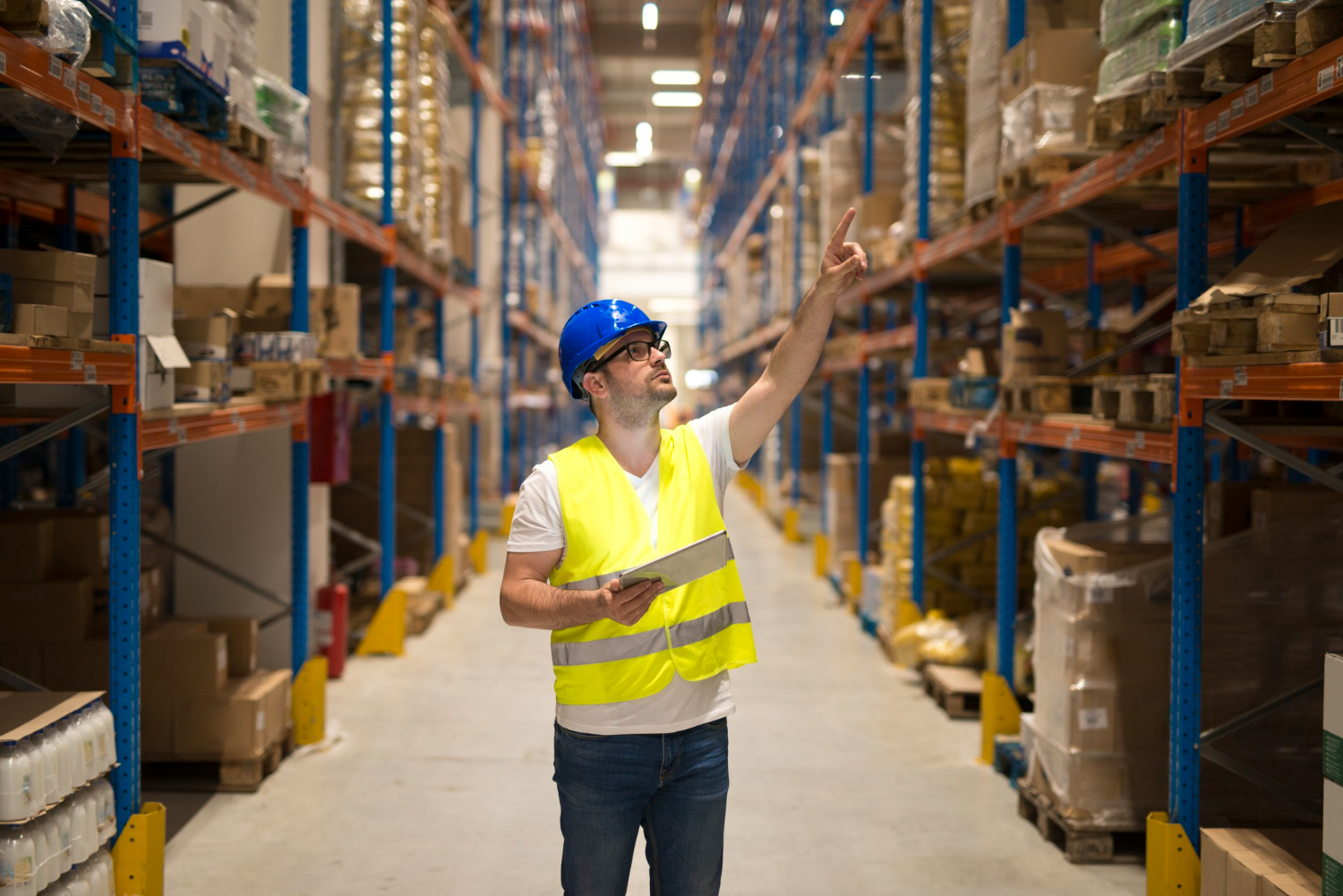
Nowadays, when customer demand is intensely customized, there is an increase in complexity in planning. Transparency and sharing of information updated in real time between customers, the factory and the supply chain allows for agility in replenishment updates and product tracking in real time, facilitating the immediate identification of problems and their resolution. Technological resources came to help manage this complex environment and eliminate waste more quickly, making companies more flexible and faster in decision-making.
An example of this is E-Kanban. In this system, tags with UWB (Ultra-wideband) technology are placed on pallets or products that can identify in real time the location of the item with accuracy within a radius of 30 cm, the number of items in process and in inventory. Any changes to the monitored parameters instantly generate an alert in a system accessible in the palm of your hand via mobile devices, wherever you are and at the time of the occurrence. The speed of technology allows for immediate problem resolution, something that previously suffered from a delay in the communication time between the perception of the problem in the process and the corrective action, often making it difficult to identify the point of occurrence of failures and extending the deadline for resolution in days or weeks. And finally, the same tag also allows recording the movement of materials, vehicles and people, enabling the analysis of the movement flow and internal logistics routes to identify and eliminate waste without the need for monitoring by a third person, whether filming or timing.

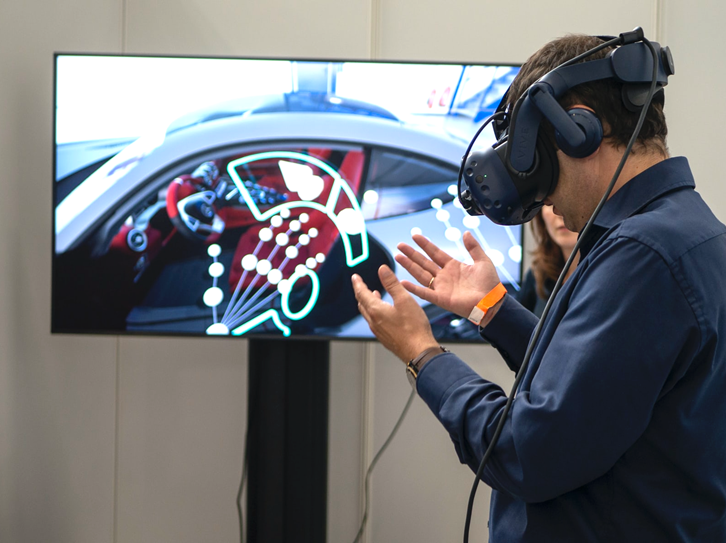
Despite being recent, augmented reality technology has also been used by companies to improve their processes. Using special glasses, employees can view work instructions, product information and quality inspection points, eliminating the risk of errors passing on to the next process. Information about the location, quantity and which item should be removed from stock is also accessible, eliminating search time, ensuring FIFO (First In First Out) and unnecessary movements. The data generated by these resources is collected and, with the use of artificial intelligence, allows the identification and analysis of time variations between operators, suggesting potential steps to be optimized in each activity cycle. Employee training can also take advantage of this technology, providing a virtual reality environment with a realistic experience of operations and simulating the maintenance of quality and productivity without generating risks to people’s safety and without using machine hours.
And remember…
For this digital transformation to occur efficiently, I recommend applying three steps presented by me at the Lean Summit Portugal in 2019:
1. Cultural Transformation, where leaders are an example for everyone and create a safe environment that allows failures for their team to exercise rapid cycles of experimentation, as part of the learning and continuous improvement process;
2. the implementation of a Scalable Transformation, focusing on the process of multiplying disseminators and problem solvers following the Lean Business Practices method;
3. finally, the application of what I call Lean Digital Intelligence, a methodology based on Lean principles combined with Artificial Intelligence solution architecture design techniques, where it is assumed that the processes are already extremely lean, robust and standardized, achieving If so, take Lean to a new level.
Having a clear purpose for using new technologies and using them according to need adds more value to processes, improves people’s activities and, most importantly, satisfies your customer. In short, digitalization and Lean create a powerful synergy that maximizes the effectiveness of the investments made by the company.
Lando Nishida
Senior Director of Honsha.ORG, co-founder of Lean Academy Portugal, speaker at Lean events in Brazil and Europe, manager trainer in more than 30 countries, certified in Smart Manufacturing by MIT and founding partner of PMLean.
Click here to read other articles from Honsha.ORG.
Follow us on YouTube.
Your Content Goes Here
Your Content Goes Here