The application of Lean methodologies and the Toyota Production System (TPS) can provide unique benefits for the energy sector, helping to optimize production processes, reduce costs, and improve the quality of the energy produced. The energy sector is one of the most important and strategic areas of the global economy, responsible for supplying electricity, fuels, and other essential products to various sectors of society.
However, energy production and distribution involve complex processes that require special attention and can lead to high costs. We will explore in a didactic manner, with examples, the unique benefits that the energy sector can gain from the implementation of these methodologies.
Reduction of Unplanned Downtime: The energy sector deals with electricity production, and it is often necessary to perform corrective maintenance on equipment and tools to prevent unplanned outages. The application of TPS can help reduce unplanned downtime by implementing standardized workflows and utilizing data analysis tools to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. For example, a power plant can employ Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) techniques to minimize equipment changeover time, thereby enhancing production efficiency.
Waste Reduction: The energy sector handles costly and hazardous materials, such as fuels and chemicals. The application of Lean can help minimize waste by ensuring that materials are stored and utilized properly. For instance, a power plant can leverage Lean principles to identify and eliminate unnecessary processes, reducing production time and preventing overproduction of energy.
Improvement in Energy Quality: The quality of produced energy is crucial for customer satisfaction and production efficiency. The application of TPS can help enhance the quality of the energy produced by reducing wait times and increasing process efficiency. For example, a power plant can use TPS to ensure that energy is produced with precision and quality, thereby increasing customer satisfaction.
Inventory Management Improvement: Inventory management is critical in the energy sector, as many materials have expiration dates and require proper storage. The application of Lean and TPS can help improve inventory management by reducing excess stock and ensuring that materials are always available for production. For instance, a power plant can implement Kanban systems to monitor fuel inventory and ensure that energy is produced quickly and efficiently.
Cost Reduction: Implementing Lean and TPS can assist in lowering costs for a power plant by eliminating waste and optimizing processes. For example, a power plant can apply Lean principles to decrease energy production time, thereby increasing employee productivity and reducing operational costs.
It is important to emphasize that each power plant has its unique characteristics and can benefit in exclusive ways from the application of these methodologies. Therefore, it is essential that implementation is carried out by specialized professionals with industry knowledge.
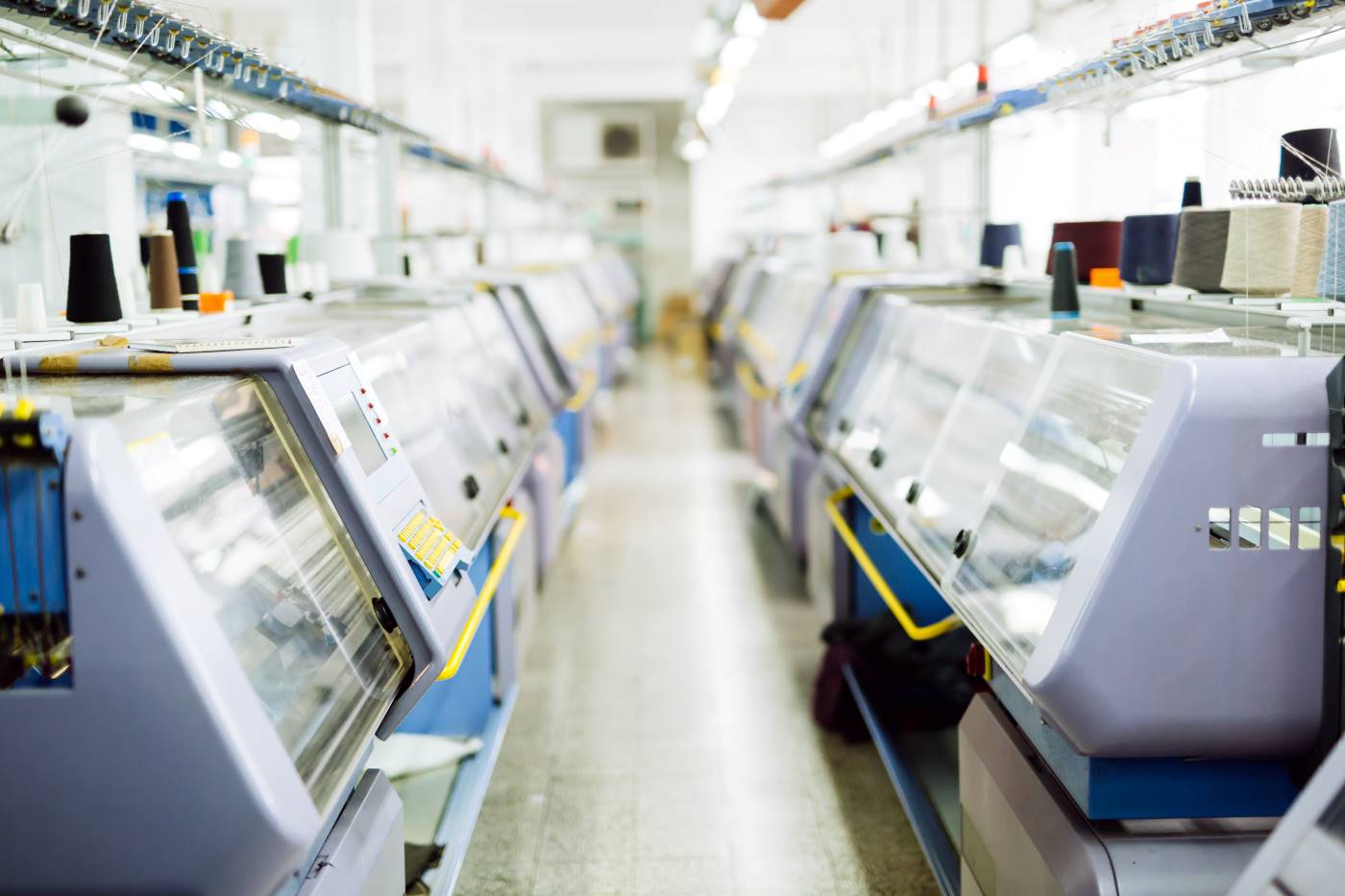
The textile sector can also experience a range of benefits from the implementation of Lean and TPS, such as reduced fabric production time, decreased waste, improved fabric quality, better inventory management, and cost reduction.
Lean methodology and the Toyota Production System (TPS) are widely utilized across various sectors of industry to enhance process efficiency, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction. However, each sector has its specificities and can gain unique advantages from the application of these methodologies.
Let’s explore how the textile sector can benefit from the implementation of Lean and TPS, leading to significant improvements in its processes and services.
Reduction of Fabric Production Time: In a textile factory, fabric production is a complex process that involves many stages. The application of Lean and TPS can help reduce fabric production time by implementing standardized workflows, utilizing Kanban to manage material flow, and employing data analysis tools to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. For example, a factory can use Kanban to monitor raw material inventory and ensure that fabrics are produced swiftly and efficiently.
Waste Reduction: The textile sector handles a large volume of materials, such as fabrics, threads, and trims. The application of Lean can help minimize waste by ensuring that fabrics are produced only in the necessary quantities and that materials are properly stored. For instance, a factory can use Lean principles to identify and eliminate unnecessary processes, reducing production time and avoiding excessive fabric production.
Improvement in Fabric Quality: The quality of fabrics is vital for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. The application of TPS can help enhance fabric quality by reducing wait times and increasing process efficiency. For example, a factory can use TPS to ensure that fabrics are produced with precision and quality, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Improvement in Inventory Management: Inventory management is crucial in the textile sector. The application of Lean and TPS can help enhance inventory management by reducing excess stock and ensuring that fabrics are always available for production. For example, a factory can apply Lean principles to decrease fabric storage time and ensure that fabrics are always fresh and ready for production.
Cost Reduction: The application of Lean and TPS can assist in lowering costs for a textile factory by eliminating waste and optimizing processes. For example, a factory can utilize Lean to reduce fabric production time, thereby increasing employee productivity and decreasing operational costs.
If you are a professional in the textile sector seeking ways to improve the efficiency and quality of your processes and services, we strongly recommend implementing these methodologies.